How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding the fundamentals of drone control, including throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll, is crucial for safe and efficient flight. Mastering these controls, along with various flight modes and the return-to-home function, ensures a smooth and controlled experience. This guide also delves into essential aspects such as pre-flight checklists, navigation strategies, photography techniques, maintenance procedures, and legal compliance, ensuring a complete understanding of responsible drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. This involves a systematic inspection of the drone and its components, as well as confirming adherence to relevant safety regulations and best practices. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to property, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight duration and ensure it is properly connected and secured.
- Propeller Inspection: Inspect each propeller for damage, ensuring they are firmly attached and free of cracks or bends. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This ensures accurate positioning and stable flight.
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Verify that the gimbal is functioning correctly and that the camera is properly mounted and secured. Test the camera’s functionality.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any visible damage or loose components.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation requires awareness and adherence to local regulations and best practices. These regulations vary by region but commonly include:
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace. Utilize apps like B4UFLY or similar tools to check airspace restrictions.
- Bystander Safety: Maintain a safe distance from people and property during operation. Avoid flying over crowds or sensitive areas.
- Line of Sight: Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times. Do not rely solely on the screen.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions, such as strong winds, rain, or fog.
- Emergency Procedures: Be prepared for emergency situations, such as battery failure or loss of control, and have a plan in place.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This checklist can be printed and used before each flight:
| Item | Checked |
|---|---|
| Battery Level | ☐ |
| Propeller Condition | ☐ |
| GPS Signal | ☐ |
| Gimbal Function | ☐ |
| Camera Function | ☐ |
| Visual Inspection | ☐ |
| Airspace Check | ☐ |
| Weather Conditions | ☐ |
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, different flight modes, and the return-to-home (RTH) function.
Basic Drone Controls
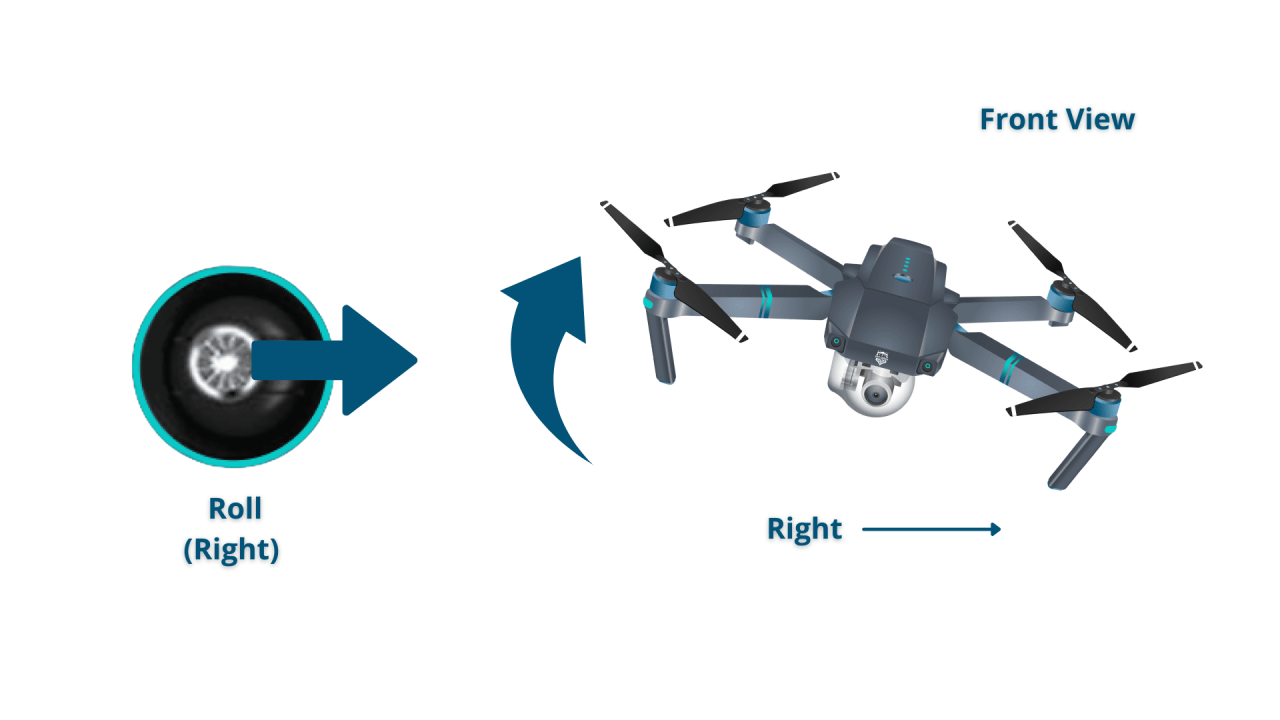
Most drones utilize four primary controls:
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls left and right movement.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability:
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Increases speed and responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for precise positioning and stability, helpful in windy conditions.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of wind conditions.
Return-to-Home (RTH) Function
The RTH function automatically returns the drone to its home point, typically the takeoff location. This is crucial in emergency situations such as low battery or loss of signal.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone smoothly into the air.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle to keep the drone at a consistent altitude.
- Landing: Slowly decrease the throttle to lower the drone gently to the ground.
Navigation and Flight Planning: How To Operate A Drone
Effective drone navigation involves understanding various methods and potential challenges. This section explores manual control, waypoint navigation, and the use of flight planning software.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Successfully navigating the airspace requires practice and a solid understanding of the regulations. For a comprehensive guide on the techniques and best practices, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
Drone Navigation Methods
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | Direct control using the controller’s sticks. | Full control, immediate responsiveness. | Requires skill, less precise for complex maneuvers. |
| Waypoint | Pre-programmed points the drone follows autonomously. | Precise flight paths, repeatable missions. | Requires planning, less adaptable to unexpected changes. |
| Autonomous | Fully automated flight using advanced features like obstacle avoidance. | Hands-free operation, complex missions possible. | Requires advanced equipment, potential for malfunctions. |
Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows for detailed mission planning, including setting waypoints, altitudes, and camera settings. This is advantageous for complex missions but requires learning the software’s interface.
Navigation Challenges
Wind conditions and GPS signal interference are significant challenges in drone navigation. Strong winds can affect stability, while GPS interference can lead to inaccurate positioning or loss of signal.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section explains how to adjust camera settings and compose compelling shots.
Camera Settings
Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for optimal image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls sensitivity to light.
Camera Angles and Shots
Drones allow for creative camera angles, including high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and tracking shots. Experiment with different perspectives to achieve visually appealing results.
Composition Techniques
Apply the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually balanced and engaging compositions. The rule of thirds divides the frame into nine equal parts, while leading lines guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
Achieving Smooth Cinematic Footage
Smooth, cinematic footage is achieved through careful flight control, using smooth movements and avoiding jerky transitions. Consider using a gimbal for added stability.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and preventing malfunctions. This section Artikels common maintenance tasks and troubleshooting steps.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Clean the drone: Regularly clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspect the propellers: Check for damage and replace worn or damaged propellers.
- Check the battery: Ensure the battery is properly charged and stored.
- Inspect the gimbal: Check for any looseness or damage.
- Update the firmware: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common malfunctions include motor failures, GPS signal loss, and battery issues. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Store your drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Use a protective case for transportation to prevent damage.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean the drone | After each flight |
| Inspect propellers | Before each flight |
| Check battery | Before each flight |
| Inspect gimbal | Weekly |
| Update firmware | Monthly |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and complying with local regulations. This section summarizes key legal aspects of drone operation.
Drone Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by region and often involve registration, licensing, and airspace restrictions. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations.
Drone Registration
Registering your drone with the relevant authorities is often mandatory. This involves providing information about your drone and yourself.
Permissions for Restricted Airspace
Obtaining necessary permissions is crucial before flying in restricted airspace, such as near airports or sensitive areas. Unauthorized flights can result in penalties.
Common Legal Pitfalls

- Flying in restricted airspace without permission.
- Failing to register your drone.
- Operating your drone beyond visual line of sight.
- Flying your drone recklessly or endangering others.
- Ignoring local laws and regulations.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, explore advanced techniques to enhance your drone skills. This section explores advanced flight techniques, FPV goggles, and advanced features.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced techniques such as precision hovering and acrobatic maneuvers require practice and skill. Start slowly and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers.
First-Person View (FPV) Goggles
FPV goggles provide an immersive flying experience, enhancing situational awareness and control. They require additional equipment and practice.
Advanced Features, How to operate a drone

Many drones offer advanced features such as obstacle avoidance and automated flight modes, simplifying complex maneuvers and enhancing safety.
Flight Paths and Maneuvers
Visualizing different flight paths and maneuvers, such as circular flights, figure-eight patterns, and complex camera movements, helps plan and execute more creative aerial shots. Careful planning and practice are essential for executing these maneuvers safely and effectively.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. This guide has provided a structured approach, from pre-flight preparation to advanced flight techniques, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience. By adhering to safety regulations, mastering drone controls, and continually refining your skills, you can unlock the full potential of this exciting technology while maintaining a commitment to responsible operation.
Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning to navigate effectively is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. This will ensure you’re comfortable and confident when operating your drone safely and efficiently.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are available. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying near metal objects or strong magnetic fields.
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight times vary widely depending on the drone model and battery size, but typically range from 15 to 30 minutes.
What should I do if I lose the GPS signal during a flight?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, carefully attempt to manually guide the drone back.
